What is C++ ?
History of C++ :
Features of C++ :
C vs C++ :
Pro's of C++ :
Con's of C++ :
Basic concepts in C++ :
Basic Input/Output :
Variable :
Rules for defining variables :
Data Types :
A data type specifies the type of data that a variable can store such as integer, floating, character etc.
if-else :
switch : switch statement executes one statement from multiple conditions.
For Loop :
//code to be executed
}
While loop :
while loop is used to iterate a part of the program several times. If the number of iteration is not fixed, it is recommended to use while loop than for loop.
Syntax : while(condition){
//code to be executed
}
Do-While Loop :
//code to be executed
}while(condition);
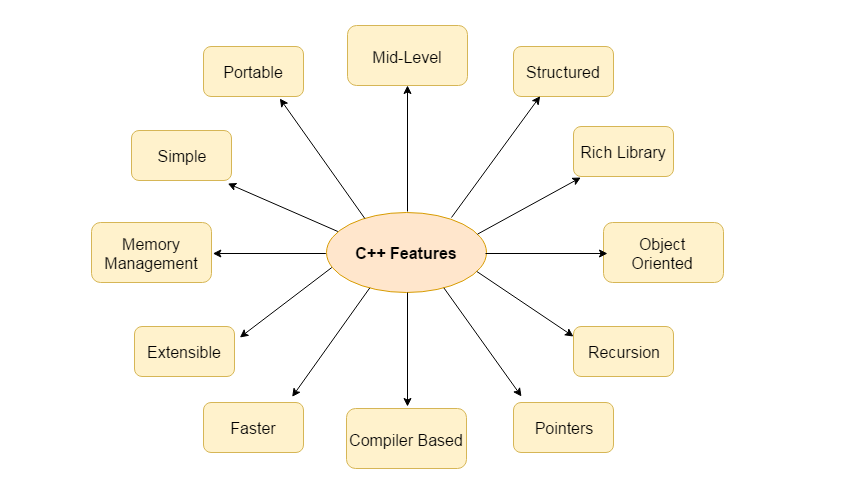
- C++ is a general purpose, case-sensitive, free-form programming language that supports object-oriented, procedural and generic programming.
- It is a middle-level language, as it encapsulates both high and low level language features.
History of C++ :
- It was developed in 1980 by Bjarne Stroustrup at bell laboratories of AT&T (American Telephone & Telegraph), located in U.S.A.
- Bjarne Stroustrup is known as the founder of C++ language.
- It was develop for adding a feature of OOP (Object Oriented Programming) in C without significantly changing the C component.
- C++ programming is "relative" (called a super set) of C.
Features of C++ :
C vs C++ :
| C | C++ |
| C follows the procedural style programming. | C++ is multi-paradigm. It supports both procedural and object oriented. |
| Data is less secured in C. | In C++, you can use modifiers for class members to make it inaccessible for outside users. |
| C follows the top-down approach. | C++ follows the bottom-up approach. |
| C does not support function overloading. | C++ supports function overloading. |
| In C, you can't use functions in structure. | In C++, you can use functions in structure. |
| C does not support reference variables. | C++ supports reference variables. |
| In C, scanf() and printf() are mainly used for input/output. | C++ mainly uses stream cin and cout to perform input and output operations. |
| Operator overloading is not possible in C. | Operator overloading is possible in C++. |
| C programs are divided into procedures and modules | C++ programs are divided into functions and classes. |
| C does not provide the feature of namespace. | C++ supports the feature of namespace. |
Pro's of C++ :
- Wide support
- Powerful
- Speed
- Small standard library
Con's of C++ :
- Unsafe
- Little memory management
- Lack of custom operators
- Complicated
Basic concepts in C++ :
Basic Input/Output :
- C++ I/O operation is using the stream concept. Stream is the sequence of bytes or flow of data. It makes the performance fast.
- If bytes flow from main memory to device like printer, display screen, or a network connection, etc, this is called as output operation.
- If bytes flow from device like printer, display screen, or a network connection, etc to main memory, this is called as input operation.
Variable :
- A variable is a name of memory location. It is used to store data. It's value can be changed and it can be reused many times.
- It is a way to represent memory location through symbol so that it can be easily identified.
- Syntax : type variable_list;
Rules for defining variables :
- A variable can have alphabets, digits and underscore.
- A variable name can start with alphabet and underscore only. It can't start with digit.
- No white space is allowed within variable name.
- A variable name must not be any reserved word or keyword e.g. char, float etc.
Data Types :
A data type specifies the type of data that a variable can store such as integer, floating, character etc.
| Types | Data Types |
| Basic Data Type | int, char, float, double, etc |
| Derived Data Type | array, pointer, etc |
| Enumeration Data Type | enum |
| User Defined Data Type | structure |
- In C++ programming, if statement is used to test the condition. There are various types of if statements in C++.
- if statement
- if-else statement
- nested if statement
switch : switch statement executes one statement from multiple conditions.
For Loop :
- The C++ for loop is used to iterate a part of the program several times. If the number of iteration is fixed, it is recommended to use for loop than while or do-while loops.
- The C++ for loop is same as C/C#. We can initialize variable, check condition and increment/decrement value.
//code to be executed
}
While loop :
while loop is used to iterate a part of the program several times. If the number of iteration is not fixed, it is recommended to use while loop than for loop.
Syntax : while(condition){
//code to be executed
}
Do-While Loop :
- do-while loop is used to iterate a part of the program several times. If the number of iteration is not fixed and you must have to execute the loop at least once, it is recommended to use do-while loop.
- The C++ do-while loop is executed at least once because condition is checked after loop body.
//code to be executed
}while(condition);